The Venn diagram of communism and capitalism presents a compelling visual representation of the overlapping and distinct characteristics of these two influential economic ideologies. By examining the shared elements and key differences between communism and capitalism, we gain a deeper understanding of their respective approaches to resource allocation, ownership, and economic growth.
Defining the Ideologies: Venn Diagram Of Communism And Capitalism
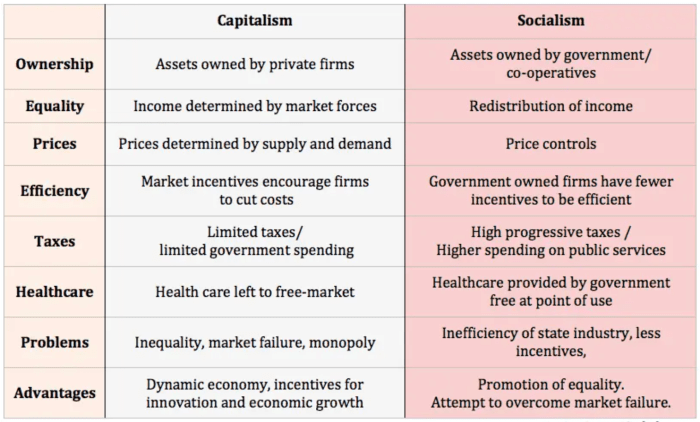
Communism and capitalism are two distinct economic and political ideologies that have shaped the course of human history. Communism is an economic system characterized by the collective ownership of property and resources, while capitalism is an economic system based on private ownership of property and resources.
Identifying the Similarities
Despite their differences, communism and capitalism share some common elements. Both ideologies strive for economic growth and stability, recognizing the importance of a productive and efficient economy. They also both emphasize the role of technology and innovation in driving economic progress.
Exploring the Differences, Venn diagram of communism and capitalism
The key difference between communism and capitalism lies in their approach to resource allocation and ownership. In communism, the government or a central authority controls the allocation of resources, while in capitalism, individuals and private entities have the freedom to own and control resources.
Creating a Venn Diagram
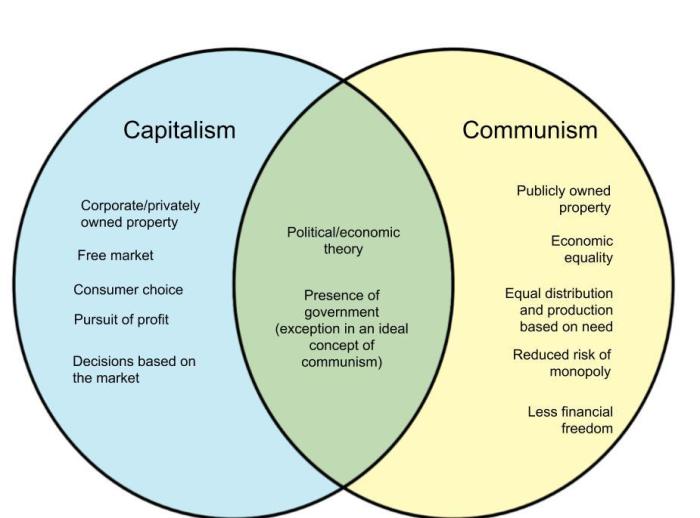
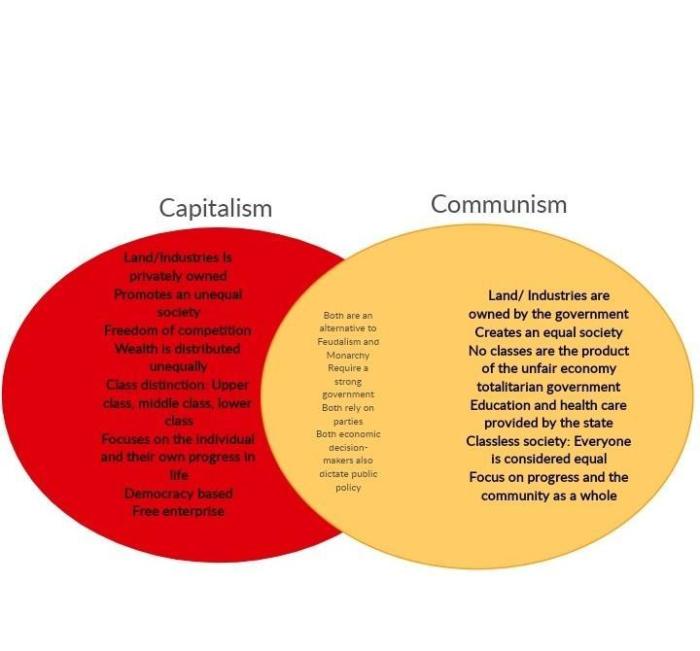
To visualize the similarities and differences between communism and capitalism, we can create a Venn diagram. The overlapping area of the diagram represents the shared elements, such as the pursuit of economic growth and stability. The non-overlapping areas represent the distinct characteristics of each ideology, such as collective ownership in communism and private ownership in capitalism.
Analyzing the Diagram
The Venn diagram highlights the key points of comparison between communism and capitalism. The overlapping area shows that both ideologies share some common goals and objectives, while the non-overlapping areas emphasize the fundamental differences in their approach to economic organization and resource allocation.
Providing Examples
Examples of communist systems include the former Soviet Union and China during the Mao Zedong era. Examples of capitalist systems include the United States, the United Kingdom, and most Western European countries. These examples illustrate the characteristics of each ideology in practice, showcasing the different approaches to resource allocation, ownership, and economic organization.
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary difference between communism and capitalism?
Communism advocates for the collective ownership of resources and central planning, while capitalism emphasizes private ownership and market-driven allocation.
How do communism and capitalism approach economic growth?
Both ideologies aim for economic growth, but they differ in their methods. Communism emphasizes planned growth, while capitalism relies on market forces and individual incentives.
Can communism and capitalism coexist?
While they are often presented as opposing ideologies, some hybrid systems incorporate elements of both communism and capitalism.