Aztecs incas and mayas mapping activity – The Aztecs, Incas, and Mayas Mapping Activity takes us on a captivating journey through the vibrant tapestry of Mesoamerican history. These three civilizations, each with its unique cultural heritage and geographical expanse, left an enduring mark on the region and beyond.
This activity invites us to delve into the fascinating world of these ancient societies, exploring their territories, cultural interactions, architectural marvels, and lasting legacies. By mapping their presence in Mesoamerica, we gain a deeper understanding of their rise, interactions, and the factors that shaped their eventual decline.
Mesoamerican Civilizations
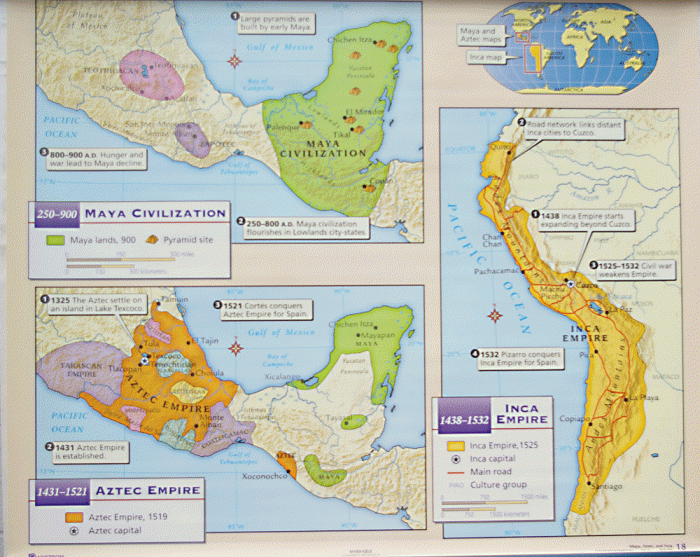
The Aztecs, Incas, and Mayas were three prominent Mesoamerican civilizations that flourished in pre-Columbian America. They played significant roles in shaping the history and culture of the region.
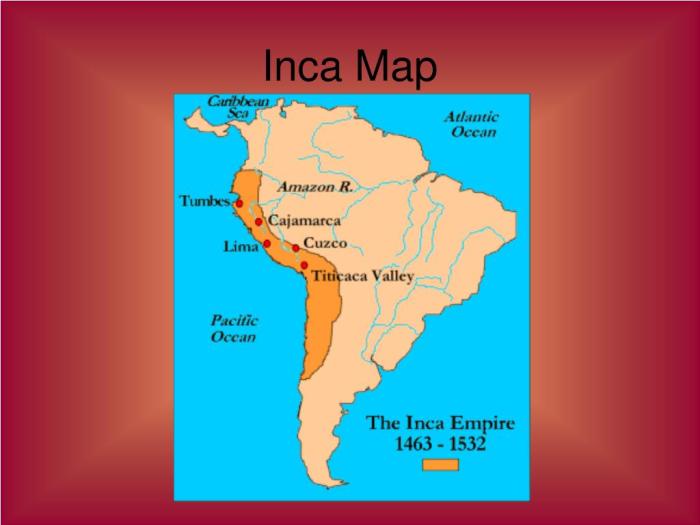
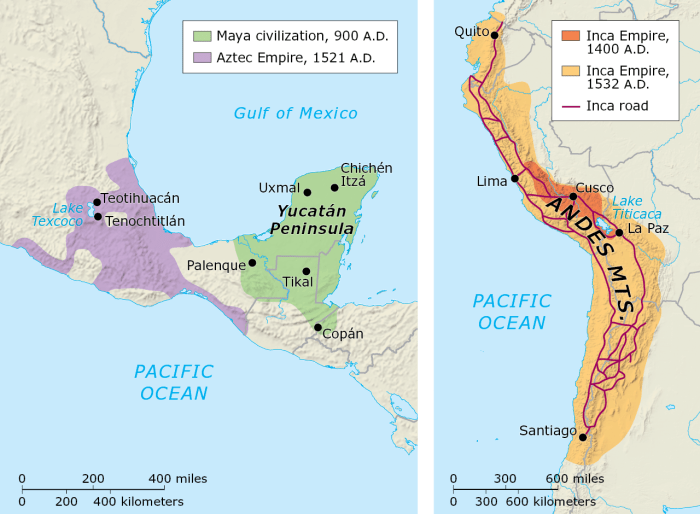
Geographically, the Aztecs occupied central Mexico, the Incas inhabited the Andean highlands of South America, and the Mayas settled in the Yucatan Peninsula and neighboring regions.
These civilizations exhibited distinct cultural characteristics. The Aztecs were known for their advanced political organization and extensive military conquests. The Incas developed an impressive road network and system of terrace farming. The Mayas possessed a sophisticated writing system and made significant advancements in mathematics and astronomy.
Factors contributing to their rise included favorable environmental conditions, technological innovations, and social organization. However, external pressures, such as European colonization and disease, ultimately led to their decline.
Mapping the Civilizations
| Civilization | Territory | Key Geographical Features |
|---|---|---|
| Aztecs | Central Mexico | – Valley of Mexico
|
| Incas | Andean highlands of South America | – Andes Mountains
|
| Mayas | Yucatan Peninsula and neighboring regions | – Lowlands and highlands
|
Cultural Interactions and Exchange

The Aztecs, Incas, and Mayas interacted and exchanged cultural influences in various ways.
Linguistically, the Mayas developed a written language known as Maya script, which was later adopted by the Aztecs and Incas for administrative purposes.
Religiously, the three civilizations shared a belief in a pantheon of gods and goddesses. However, their specific deities and practices differed.
Socially, the Aztecs and Incas established complex hierarchical systems, while the Mayas had a more decentralized political structure.
These interactions contributed to the cultural development of each civilization, leading to the exchange of knowledge, technology, and artistic ideas.
Answers to Common Questions: Aztecs Incas And Mayas Mapping Activity
What is the significance of the Aztecs, Incas, and Mayas in Mesoamerican history?
These civilizations were highly advanced societies that made significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, architecture, and art. They also developed complex political and economic systems that influenced the development of Mesoamerica.
What factors contributed to the rise and eventual decline of these civilizations?
Various factors, including environmental changes, warfare, disease, and internal conflicts, played a role in the rise and fall of these civilizations. The Aztecs, for example, were conquered by the Spanish in the 16th century, while the Incas and Mayas experienced internal strife and environmental challenges that led to their decline.
How did the Aztecs, Incas, and Mayas interact with each other?
There was limited direct interaction between the Aztecs and the Incas, as they were separated by a vast distance. However, the Mayas had significant cultural and trade interactions with both the Aztecs and the Incas, exchanging goods, ideas, and technologies.