Delve into the fascinating world of chemistry with periodic table of elements brainpop, an interactive learning platform that unlocks the secrets of the periodic table. Embark on a journey through the elements, discovering their properties, periodic trends, and countless applications.
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, serves as a systematic arrangement of elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties. Its intuitive organization allows scientists to predict the behavior of elements and uncover the fundamental principles governing the universe.
Periodic Table Overview
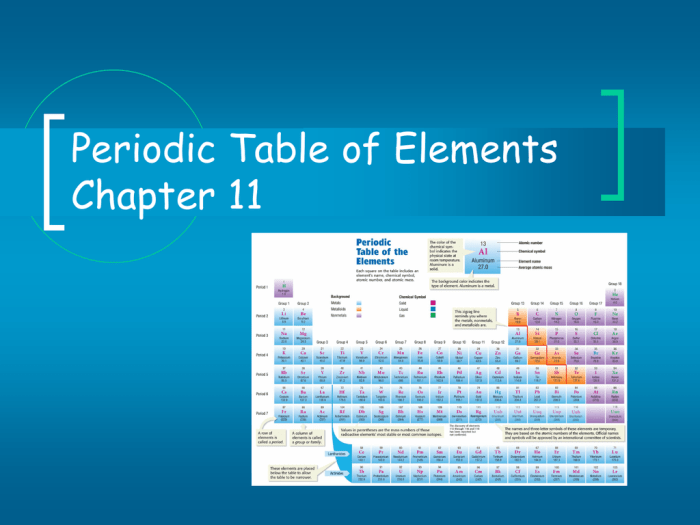
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It is a powerful tool for predicting and understanding the behavior of elements and their compounds.
Table Organization
The periodic table is organized into 18 vertical columns, known as groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. The groups are numbered 1-18 from left to right, while the periods are numbered 1-7 from top to bottom.
| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period 1 | H | He | ||||||||||||||||
| Period 2 | Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||
| Period 3 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||
| Period 4 | K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| Period 5 | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| Period 6 | Cs | Ba | * | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| Period 7 | Fr | Ra | * | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og |
*Lanthanide and actinide elements are placed below the main table.
Groups and Periods
The elements in the periodic table are grouped based on their chemical properties. Elements in the same group share similar electron configurations and, therefore, have similar chemical properties.
The periods represent the number of electron shells in the atoms of the elements. As you move from left to right across a period, the number of electrons in the outermost shell increases, leading to changes in chemical properties.
Element Properties
The chemical properties of elements are determined by their atomic number, atomic mass, and electron configuration. These properties influence how elements behave and interact with each other.
Atomic Number
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in its nucleus. It determines the element’s identity and position on the periodic table. Elements with the same atomic number are isotopes of each other, meaning they have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Atomic Mass
The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of all its naturally occurring isotopes. It is expressed in atomic mass units (amu) and is used to calculate the molar mass of compounds.
Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of an element describes the arrangement of its electrons in atomic orbitals. This configuration determines the element’s chemical reactivity and bonding behavior. Elements with similar electron configurations tend to have similar chemical properties.
Applications of Element Properties
- Nuclear Power:The atomic number and mass of uranium and plutonium isotopes are crucial for nuclear reactions in power plants.
- Medicine:The atomic number of elements like iodine and cobalt is used in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
- Materials Science:The electron configuration of elements determines their electrical and thermal properties, which are essential for designing electronic devices and alloys.
Periodic Trends
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number, revealing periodic trends in their properties. These trends include atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy, which vary systematically across the table.
Atomic radius generally decreases from left to right across a period (row) and increases from top to bottom within a group (column). Electronegativity increases from left to right and decreases from top to bottom. Ionization energy, the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, generally increases from left to right and decreases from top to bottom.
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. It decreases across a period because the increasing nuclear charge attracts the electrons more strongly, pulling them closer to the nucleus. Within a group, atomic radius increases down the table as new electron shells are added.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It increases across a period due to the increasing nuclear charge, which makes the nucleus more attractive to electrons. Electronegativity decreases down a group as the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons increases, reducing the nucleus’s attraction for electrons.
Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. It generally increases across a period because the increasing nuclear charge makes it more difficult to remove an electron. Ionization energy decreases down a group as the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons increases, making it easier to remove an electron.
Applications of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a powerful tool that has been used to advance our understanding of the world around us. It has led to the development of new materials, the discovery of new elements, and the creation of new technologies.
The periodic table is used in a wide variety of fields, including chemistry, physics, and biology. In chemistry, the periodic table is used to predict the properties of elements and to understand how they react with each other. In physics, the periodic table is used to understand the structure of atoms and the behavior of electrons.
In biology, the periodic table is used to understand the role of elements in living organisms.
Specific Examples, Periodic table of elements brainpop
The periodic table has been used to make many important scientific discoveries and technological advancements. For example, the periodic table was used to discover the noble gases, which are used in a variety of applications, such as lighting and refrigeration.
The periodic table was also used to develop the transistor, which is the foundation of modern electronics.
Role in Understanding Matter
The periodic table is a key tool for understanding the structure and properties of matter. The periodic table shows how the elements are arranged in a way that reflects their properties. This arrangement allows us to predict the properties of new elements and to understand how they will behave in different situations.
History and Evolution of the Periodic Table

The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. Its history spans over a century, with significant contributions from various scientists who refined and expanded our understanding of the elements and their organization.
Early Development
The concept of organizing elements based on their properties emerged in the early 19th century. In 1817, Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner proposed the law of triads, which grouped elements with similar properties into sets of three. In 1864, John Newlands arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic mass, noticing a pattern of repeating properties every eight elements, which he called the law of octaves.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev published the first widely recognized periodic table. Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass, and grouped them into vertical columns (groups) and horizontal rows (periods) based on their chemical properties. Mendeleev’s table was groundbreaking, as it predicted the existence of undiscovered elements and accurately predicted their properties.
Henry Moseley’s Contribution
In 1913, Henry Moseley discovered the concept of atomic number, which is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. Moseley’s work led to the realization that atomic number, rather than atomic mass, was the fundamental basis for organizing the elements.
This discovery led to a revised periodic table that more accurately reflected the chemical properties of the elements.
Modern Periodic Table
The modern periodic table is based on the work of Mendeleev and Moseley. It consists of 18 vertical columns (groups) and 7 horizontal rows (periods). The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, with elements in the same group sharing similar chemical properties.
The periodic table has been continually updated as new elements are discovered and our understanding of the elements evolves.
Detailed FAQs: Periodic Table Of Elements Brainpop
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
Who developed the periodic table?
The modern periodic table is largely attributed to Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, who published his first version in 1869.
What are the different groups and periods in the periodic table?
The periodic table is divided into 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
What are some applications of the periodic table?
The periodic table is used in various fields, including chemistry, physics, biology, and materials science. It helps scientists predict the properties of elements, design new materials, and understand the behavior of atoms and molecules.