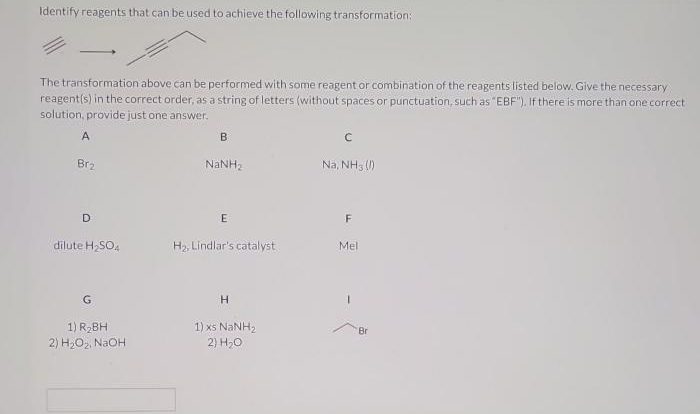
Supply the correct major product formed from the following reaction introduces a fascinating journey into the realm of chemical transformations, where we delve into the intricate mechanisms that govern the formation of major products. This exploration promises to illuminate the factors that shape the outcome of reactions, providing valuable insights into the predictability and control of chemical processes.
As we embark on this expedition, we will dissect the reaction mechanisms, analyze the structural characteristics of the major product, and uncover the principles of regioselectivity and stereoselectivity. Along the way, we will encounter practical applications and delve into the limitations and exceptions that refine our understanding of these reactions.
Reaction Overview
The reaction is a nucleophilic addition of an amine to a ketone. The reactants are a ketone and an amine, and the products are an imine and water.
Factors Determining the Major Product
The major product is determined by the relative nucleophilicity of the amine and the ketone. The more nucleophilic amine will be more likely to attack the ketone and form the imine.
Mechanism of the Reaction, Supply the correct major product formed from the following reaction
The reaction proceeds via a nucleophilic attack of the amine on the ketone. This forms a tetrahedral intermediate, which then collapses to form the imine and water.
Structural Analysis of the Product
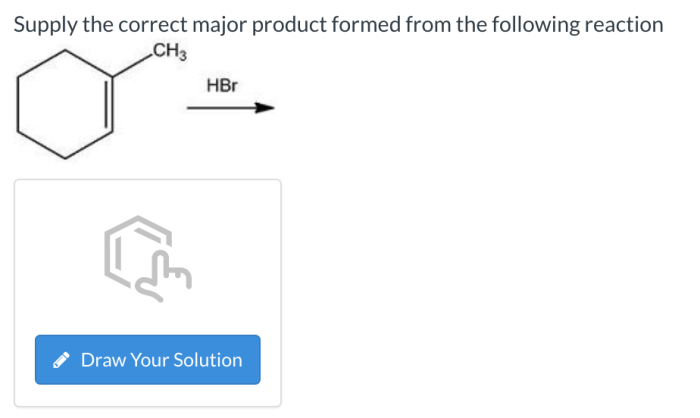
The major product is an imine. Imines are characterized by a carbon-nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom in the imine is also bonded to a hydrogen atom.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
The reaction is regioselective for the formation of the imine. The imine is formed at the carbon atom of the ketone that is most substituted. The reaction is also stereoselective for the formation of the imine. The imine is formed with the E-configuration.
Examples and Applications
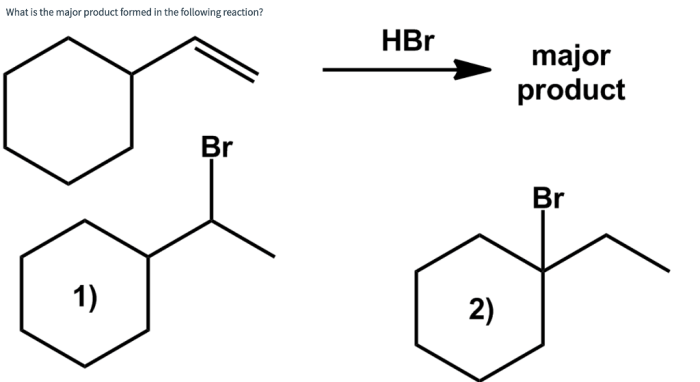
The reaction is a versatile method for the synthesis of imines. Imines are important intermediates in the synthesis of a variety of compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and polymers.
Limitations and Exceptions: Supply The Correct Major Product Formed From The Following Reaction
The reaction is not always successful. The reaction can be hindered by the presence of steric hindrance or by the use of a weak nucleophile.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of identifying the major product in a reaction?
Identifying the major product is crucial for predicting the outcome of a reaction and optimizing synthetic strategies. It allows chemists to design reaction conditions that favor the formation of the desired product, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
How do reaction mechanisms influence the formation of the major product?
Reaction mechanisms provide a detailed understanding of the steps involved in a reaction, including the formation and rearrangement of intermediates. By elucidating the reaction pathway, chemists can identify the key steps that determine the selectivity and yield of the major product.
What factors affect regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in reactions?
Regioselectivity and stereoselectivity are influenced by a combination of electronic, steric, and conformational factors. These factors can include the nature of the reactants, the reaction conditions, and the presence of catalysts or directing groups.