Embark on a scientific expedition with the cell respiration worksheet answer key, your guide to unraveling the intricate processes that fuel life. This comprehensive resource empowers you to delve into the depths of cellular respiration, unlocking the secrets of energy production that sustain every living organism.
Through a meticulous analysis of the worksheet’s structure, key concepts, and real-world applications, you’ll gain a profound understanding of this fundamental biological process.
Cell Respiration Overview: Cell Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
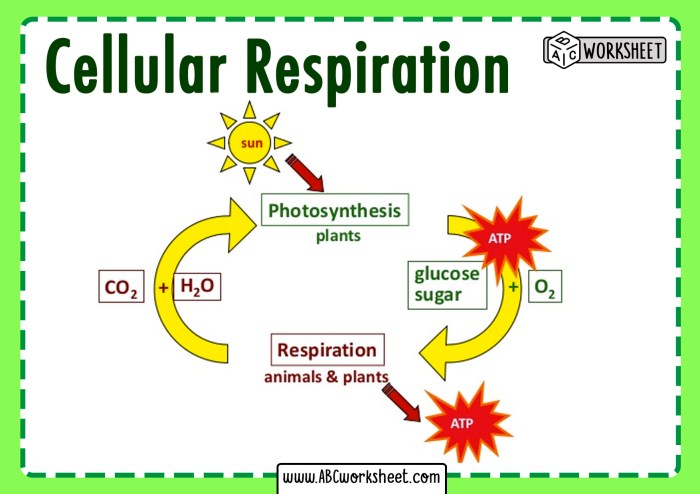
Cell respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. This process is essential for the survival of all living organisms because ATP serves as the main energy currency for cells.
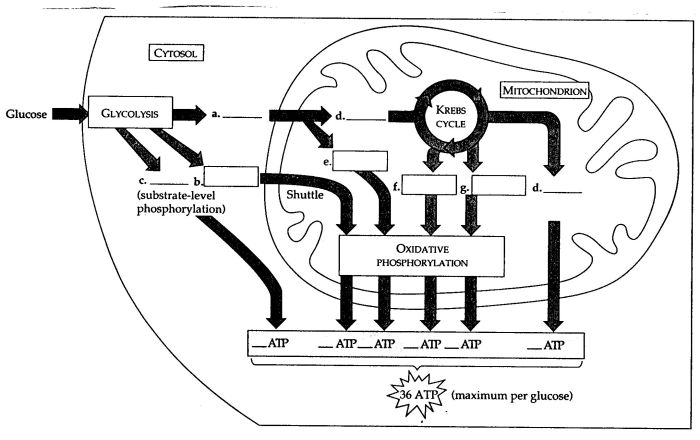
Cellular respiration occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, along with a net production of two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH.
Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. In this cycle, the pyruvate molecules produced during glycolysis are further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide as a waste product and generating NADH, FADH2, and ATP molecules.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the final stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. During oxidative phosphorylation, the NADH and FADH2 molecules produced in the previous stages are used to generate a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
This gradient is then used to drive the synthesis of ATP through ATP synthase.
Worksheet Analysis
The cell respiration worksheet focuses on understanding the process of cellular respiration, including its stages, reactants, products, and energy yield.
The objectives of the worksheet are to:
- Define cell respiration and identify its importance.
- Describe the three main stages of cell respiration: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
- Identify the reactants and products of each stage of cell respiration.
- Calculate the energy yield of cell respiration.
- Apply knowledge of cell respiration to real-world scenarios.
Types of Questions and Exercises
The worksheet includes a variety of question types and exercises to assess students’ understanding of cell respiration, including:
- Multiple choice questions:These questions test students’ knowledge of the basic concepts of cell respiration.
- Short answer questions:These questions require students to explain the process of cell respiration in their own words.
- Diagram labeling:This exercise requires students to label a diagram of the cell respiration process.
- Problem-solving questions:These questions require students to apply their knowledge of cell respiration to real-world scenarios.
Answer Key Structure
The answer key provides the correct responses to the questions or problems in the worksheet. It is typically organized in the same order as the worksheet, with each answer corresponding to the respective question or problem.
Using an answer key for self-assessment and learning is significant for several reasons:
Checking Understanding
- It allows students to assess their understanding of the concepts and skills covered in the worksheet.
- By comparing their responses to the correct answers, students can identify areas where they need further clarification or practice.
Feedback and Reinforcement
- The answer key provides immediate feedback on student performance.
- Correct answers reinforce students’ understanding and encourage them to continue studying the material.
- Incorrect answers indicate areas where students need to revisit the concepts and practice more.
Facilitating Learning
- Answer keys can be used as a study guide, helping students review the material and reinforce their understanding.
- They can also be used by teachers to provide additional support and guidance to students who need it.
Key Concepts and Terminology
Cellular respiration, a complex biochemical process occurring within cells, is crucial for energy production and sustaining life. To grasp this process fully, it is essential to understand the fundamental concepts and terminology associated with it.
Key concepts and terms related to cellular respiration include:
Glycolysis
- The initial stage of cellular respiration, occurring in the cytoplasm, where glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Produces a net gain of 2 molecules of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), 2 molecules of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), and 2 molecules of pyruvate.
Pyruvate Oxidation
- Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, where pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA, a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
- Produces 1 molecule of NADH and 1 molecule of CO2 (carbon dioxide).
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
- A series of enzymatic reactions that occur in the mitochondrial matrix, where acetyl-CoA is further oxidized to produce energy.
- Produces 3 molecules of NADH, 1 molecule of FADH2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide), and 1 molecule of ATP per acetyl-CoA molecule.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
- A series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where NADH and FADH2 are oxidized to pump protons across the membrane.
- The resulting proton gradient drives ATP synthesis through ATP synthase, the final step in cellular respiration.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
- The process by which ATP is generated as protons flow back across the inner mitochondrial membrane through ATP synthase.
- Produces the majority of ATP (32-34 molecules) during cellular respiration.
Application and Examples
Cellular respiration plays a crucial role in the survival and functioning of all living organisms. It provides the energy necessary for various cellular processes, including growth, movement, and reproduction.
Table of Cellular Respiration Stages
The process of cellular respiration can be divided into three main stages:
- Glycolysis: Occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into pyruvate, releasing a small amount of energy.
- Krebs cycle (Citric acid cycle): Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and further breaks down pyruvate, releasing carbon dioxide and generating energy-rich molecules.
- Electron transport chain: Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, it utilizes the energy-rich molecules from the Krebs cycle to produce ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell.
Real-World Applications
Cellular respiration has numerous applications in the real world, including:
- Energy production:Cellular respiration is the primary mechanism by which organisms generate energy for cellular activities, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis.
- Food preservation:Respiration can be manipulated to extend the shelf life of food products. For example, controlled atmosphere storage reduces oxygen levels to slow down respiration and preserve freshness.
- Biofuel production:Cellular respiration is harnessed in the production of biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, which are renewable and environmentally friendly alternatives to fossil fuels.
- Medical diagnostics:Cellular respiration can be used as a diagnostic tool to assess mitochondrial function in diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
Misconceptions and Common Errors
When studying cellular respiration, students may encounter several misconceptions or errors. Addressing these misconceptions is crucial for promoting accurate understanding of this fundamental biological process.
Misconception 1, Cell respiration worksheet answer key
Misconception:Cellular respiration only occurs in plants.
Correction:Cellular respiration occurs in all living organisms, including animals, plants, and microorganisms. It is essential for energy production in all cells.
Misconception 2
Misconception:Glycolysis is the only stage of cellular respiration that requires oxygen.
Correction:Only the citric acid cycle and electron transport chain require oxygen. Glycolysis, the first stage, occurs without oxygen (anaerobic respiration).
Misconception 3
Misconception:ATP is produced in equal amounts during glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Correction:The electron transport chain produces the majority of ATP (about 32 molecules per glucose molecule), while glycolysis yields only 2 molecules and the citric acid cycle 2 molecules.
Misconception 4
Misconception:Cellular respiration is 100% efficient in converting glucose to energy.
Correction:Cellular respiration is not fully efficient, with about 68% of the energy in glucose converted to ATP. The remaining energy is lost as heat.
Additional Resources and Extensions
Enhancing the understanding of cellular respiration beyond the confines of the worksheet can be achieved through the incorporation of additional resources and extension activities.
Exploring the connections between cellular respiration and other biological concepts deepens the comprehension of its significance in the broader context of life processes.
Interactive Simulations and Visualizations
- Interactive simulations and visualizations, such as those found on websites like Khan Academy and PBS LearningMedia , provide an engaging and interactive way to explore the processes involved in cellular respiration.
- These resources allow students to visualize the steps of cellular respiration, manipulate variables, and observe the effects of different conditions on the process.
Connections to Other Biological Concepts
- Connecting cellular respiration to other biological concepts, such as photosynthesis, energy metabolism, and nutrient cycling, helps students understand its role in the larger context of life processes.
- For example, exploring the relationship between cellular respiration and photosynthesis highlights the interconnectedness of living organisms and the flow of energy within ecosystems.
FAQ Section
What is the primary function of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert nutrients into energy, primarily in the form of ATP.
What are the key stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation are the three main stages of cellular respiration.
How does the answer key facilitate learning?
The answer key provides instant feedback, allowing you to assess your understanding, identify areas for improvement, and reinforce your knowledge.